Hedge funds are investment vehicles that pool money from accredited investors and use various strategies to generate high returns. These funds are typically managed by professional fund managers and are known for their flexibility and ability to invest in a wide range of assets.
With their focus on aggressive growth, hedge funds often employ complex trading techniques and take both long and short positions in the market. While they offer the potential for significant profits, hedge funds also come with higher risks and are subject to less regulation compared to traditional investment funds.
Understanding the basics of hedge funds can help investors make informed decisions about their investment portfolios.
The Essence Of Hedge Funds
Defining Hedge Funds
A hedge fund is an investment fund that pools capital from accredited individuals or institutional investors and invests in a diverse range of assets.
Key Characteristics
Hedge funds typically employ various investment strategies and are known for their flexibility, aggressive approach, and ability to generate returns in both rising and falling markets.
Historical Perspective
Gain insights into hedge funds through a historical lens to understand their evolution and impact on financial markets. Uncover the essential aspects of hedge funds to navigate this complex investment landscape effectively.
Origins And Evolution
Let’s dive into the historical perspective of hedge funds. These investment vehicles have a fascinating origin and have evolved significantly over time. Understanding their roots can provide valuable insights into their purpose and function in today’s financial landscape.
In the mid-20th century, hedge funds emerged as a response to the changing dynamics of the investment world. Alfred Winslow Jones is credited with establishing the first hedge fund in 1949. Jones introduced a unique investment strategy that involved both long and short positions, aiming to mitigate risk and generate returns regardless of market conditions.
This approach was a departure from traditional investment funds that focused solely on long positions. Jones’s innovative strategy laid the groundwork for what would become the hallmark of hedge funds – the ability to both buy and sell securities, enabling investors to profit from both upward and downward market movements.
Influential Figures In Hedge Fund History
Several influential figures have shaped the history of hedge funds. Let’s take a closer look at some key individuals who have left a lasting impact on the industry:
- George Soros: Known for his successful currency speculation and philanthropic endeavors, Soros is widely regarded as one of the most prominent hedge fund managers in history. His Quantum Fund gained significant attention with its ability to generate substantial returns through strategic investments.
- Paul Tudor Jones: Jones gained recognition for predicting the stock market crash of 1987. His fund, the Tudor Investment Corporation, utilized macroeconomic analysis and technical indicators to identify investment opportunities. Jones’s market insights and risk management skills have made him a highly respected figure in the hedge fund world.
- Ray Dalio: Dalio founded Bridgewater Associates, one of the world’s largest hedge funds. His investment philosophy, based on a deep understanding of economic cycles and principles, has propelled Bridgewater to great success. Dalio’s emphasis on radical transparency and a systematic approach to decision-making has set him apart within the industry.
These influential figures have not only achieved remarkable financial success but have also contributed to the evolution and innovation within the hedge fund space. Their strategies and approaches have inspired countless investors and continue to shape the industry today.
Hedge Funds Vs. Traditional Investments
Explore the differences between Hedge Funds and Traditional Investments. Gain insights into Hedge Funds: What You Need to Know.
Comparing Strategies And Performance
Hedge funds and traditional investments are two different ways to invest money. Hedge funds are managed by professional portfolio managers who use a variety of investment strategies to achieve positive returns. In contrast, traditional investments usually involve buying and holding stocks, bonds, and other assets for the long term. Hedge funds tend to have a more active investment approach, while traditional investments rely on a passive approach. The performance of hedge funds is often measured against benchmarks, such as the S&P 500, while traditional investments are typically measured against their respective indices.
Risk And Return Profiles
Hedge funds and traditional investments also have different risk and return profiles. Hedge funds tend to have higher risk and higher potential returns compared to traditional investments. This is because hedge funds often use leverage and invest in riskier assets, such as derivatives and commodities. Traditional investments, on the other hand, are typically more conservative and invest in blue-chip stocks and high-quality bonds. As a result, traditional investments tend to have lower risk and lower potential returns compared to hedge funds.
In summary, hedge funds and traditional investments are two different ways to invest money with different strategies, risk, and return profiles. Hedge funds often have a more active investment approach, higher risk, and higher potential returns, while traditional investments are typically more conservative with a passive investment approach, lower risk, and lower potential returns. It’s important to understand the differences between these investment options and choose the one that aligns with your investment goals and risk tolerance.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/hedge-fund-e24f63dddbea46509acc50e93e12132f.jpg)
Credit: www.investopedia.com
Common Hedge Fund Strategies
Explore the world of hedge fund strategies, including long/short equity, global macro, and event-driven approaches. These strategies aim to deliver high returns by leveraging various market opportunities and mitigating risk through diversification and sophisticated techniques. Understanding these strategies is essential for investors looking to navigate the complex landscape of hedge funds.
Common Hedge Fund Strategies are used by hedge fund managers to generate returns for their investors. These strategies involve various techniques and approaches, each with its own unique characteristics and risk levels. Here are some of the most popular Common Hedge Fund Strategies:
Long/Short Equity
Long/Short Equity strategy is a popular hedge fund strategy that involves buying undervalued stocks and short-selling overvalued stocks. This strategy aims to generate returns by taking advantage of the market’s mispricing of securities. The long position is taken in stocks that are expected to increase in value, while the short position is taken in stocks that are expected to decrease in value. This strategy is particularly effective in volatile markets.
Market Neutral
Market Neutral is a strategy that involves taking both long and short positions in equal amounts, with the aim of neutralizing the market risk. This strategy seeks to generate returns by taking advantage of the differences in the valuation of related securities. The focus is on identifying pairs of stocks that are highly correlated and investing in the undervalued stock while short-selling the overvalued stock.
Global Macro
Global Macro is a strategy that involves taking positions in various financial instruments based on macroeconomic analysis and forecasts. This strategy aims to generate returns by taking advantage of global economic trends and events. Global Macro hedge fund managers use various techniques such as currency trading, commodity trading, and interest rate trading to take advantage of the global economic environment.
In conclusion, hedge fund strategies are complex and require a high level of expertise and knowledge to implement successfully. Each strategy has its own unique characteristics and risk levels, and investors should carefully consider these factors before investing in hedge funds.
Analyzing Hedge Fund Performance
Learn all about analyzing hedge fund performance to understand key concepts and strategies in hedge fund investments. Gain insights into evaluating the effectiveness and success of hedge funds. Stay informed on industry trends and make informed decisions to optimize your investment portfolio.
Benchmarks And Metrics
Transparency And Reporting
Understanding Hedge Fund Performance is crucial for investors. Hedge Funds use various benchmarks and metrics to evaluate performance.
Benchmarks provide a standard for comparison. They measure Hedge Funds against similar investments. Metrics include returns, volatility, and risk-adjusted performance.
Transparency is essential for investors. They rely on reporting to understand the fund’s strategy, risks, and performance. Clear reporting builds trust.
.webp)
Credit: www.geeksforgeeks.org
Investor Qualifications
Investor Qualifications play a crucial role in hedge fund investments, ensuring that only eligible individuals or entities participate in these high-risk, high-reward ventures. Understanding the criteria for becoming an investor in a hedge fund is essential for anyone considering entering this exclusive market. Below, we delve into the two key aspects of investor qualifications: Accredited Investors and Minimum Investment Thresholds.
Accredited Investors
Accredited Investors are individuals or entities that meet specific income or net worth requirements, as outlined by securities regulations. In the United States, an accredited investor is defined as someone with an annual income exceeding $200,000 (or $300,000 for joint income) for the past two years, with a reasonable expectation of the same income in the current year. Alternatively, an individual with a net worth exceeding $1 million, either individually or jointly with a spouse, qualifies as an accredited investor. These criteria are designed to ensure that only financially sophisticated and high-net-worth individuals gain access to hedge funds, which often involve complex and risky investment strategies.
Minimum Investment Thresholds
Minimum Investment Thresholds are the minimum amount of capital required to participate in a hedge fund. These thresholds are set by the fund managers and can vary widely, ranging from tens of thousands to millions of dollars. Hedge funds typically have high minimum investment requirements, often in the hundreds of thousands of dollars, to ensure that only serious and financially capable investors are involved. By setting these thresholds, hedge funds aim to attract committed and financially qualified individuals while also managing the fund’s overall size and investor base.
The Regulatory Landscape
When it comes to understanding hedge funds, navigating the regulatory landscape is crucial. Let’s delve into the domestic and international regulations that govern these investment vehicles.
Domestic And International Regulations
Domestic regulations pertain to laws within a specific country. These can include registration requirements for hedge fund managers.
International regulations encompass rules that span across borders. Hedge funds operating in multiple countries must adhere to these regulations.
Impact Of Financial Crises On Oversight
Financial crises have led to stricter oversight of hedge funds. Regulators aim to prevent risks that could destabilize the financial system.
Increased scrutiny post-crises has resulted in enhanced reporting requirements for hedge funds. This ensures transparency and accountability.
Future Trends In Hedge Funds
Hedge funds are evolving rapidly, driven by technological advancements and changing investor sentiments. Let’s explore the future trends shaping the landscape:
Technological Advances
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning are revolutionizing hedge fund operations.
Algorithmic trading is becoming more prevalent in hedge fund strategies.
Big data analytics is enabling hedge funds to make more informed investment decisions.
Shifting Investor Sentiments
The growing interest in sustainable investing is influencing hedge fund strategies.
Increased focus on transparency and governance is reshaping investor expectations.
The rise of social impact investing is a key trend in the hedge fund industry.
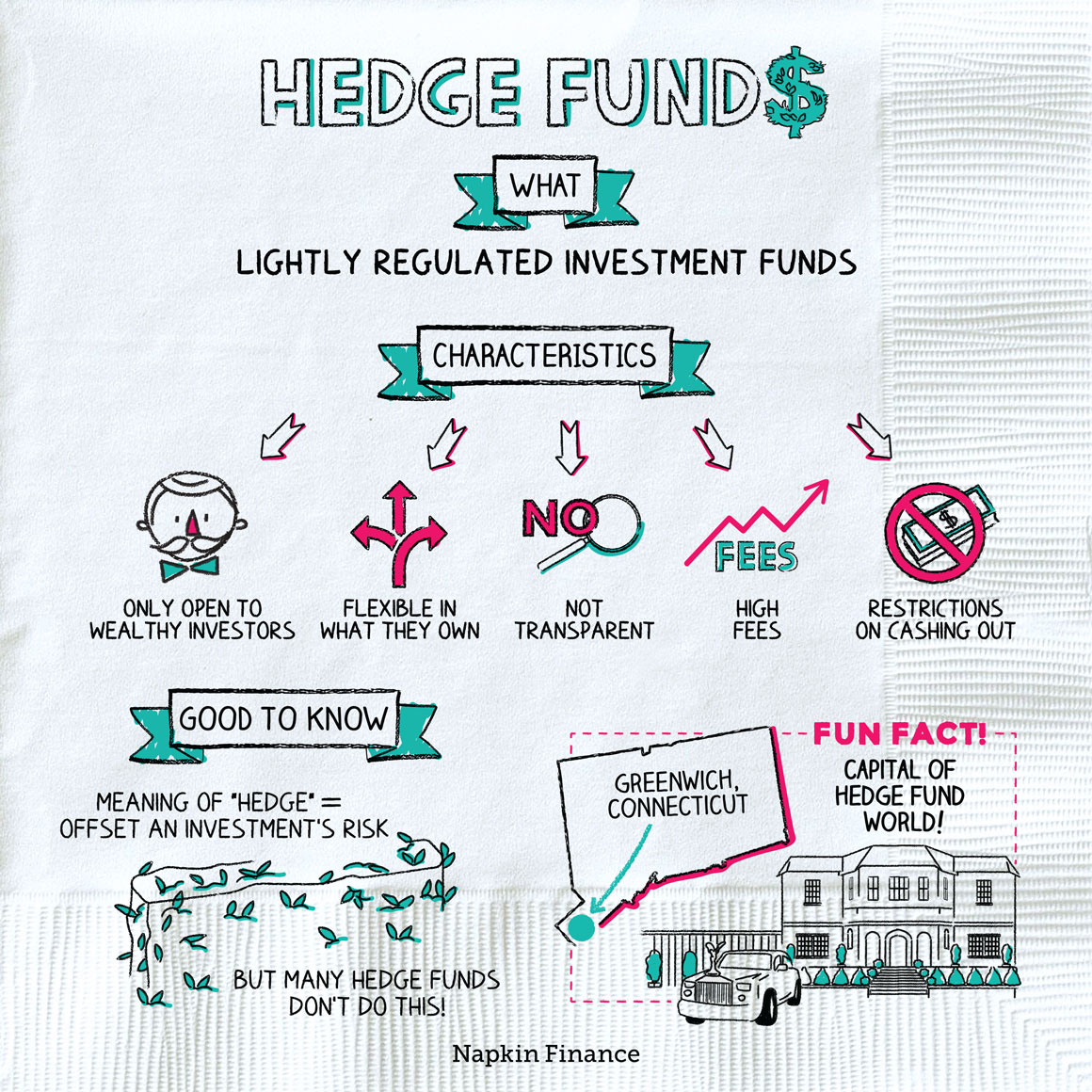
Credit: napkinfinance.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Do You Need To Know About Hedge Funds?
Hedge funds are private investment funds that pool money from wealthy investors. They aim to generate high returns through a variety of investment strategies, such as leveraging, short-selling, and derivatives trading. Hedge funds are less regulated than traditional investments, and investors must meet certain income and net worth requirements to participate.
It’s important to carefully research and understand the risks involved before investing in hedge funds.
What Is The 2 20 Rule For Hedge Funds?
The 2/20 rule for hedge funds is a compensation structure where hedge fund managers receive a 2% management fee and a 20% performance fee. The management fee is a percentage of assets under management, while the performance fee is a percentage of the profits earned by the fund.
This compensation structure is designed to align the interests of the manager with those of the investors.
How Much Money Do You Need To Be Considered A Hedge Fund?
To be considered a hedge fund, the minimum amount of money required varies but is generally several million dollars. The specific amount depends on factors like the fund’s investment strategy and regulatory requirements.
How Much Net Worth Do You Need To Have To Be In A Hedge Fund?
To be in a hedge fund, you typically need a net worth of at least $1 million.
Conclusion
To sum up, understanding hedge funds is essential for anyone looking to explore investment opportunities. By grasping the key concepts and strategies behind these alternative investments, you can make informed decisions to potentially maximize your returns. Remember, hedge funds offer unique advantages but also come with risks.
So, always consult with a financial advisor to ensure your investment aligns with your goals and risk tolerance. Happy investing!






